Download and print the infographic [PDF – 664 KB]

Hospitalization:
A Major Risk Factor for Dangerous Blood Clots
Roughly 1 out of 10
hospital deaths are
related to blood
clots in the lungs.
Blood clots are a
leading cause of
preventable hospital
death in the United States.
Prevent the Need for 911. Get the Facts on Blood Clots.
About half of all blood clots occur during or within 3 months of a hospital stay or surgery
Many of these blood clots can be safely prevented
Nearly half of all hospital patients do not receive proper prevention measures
Know Your Risk: The Link Between Hospitalization and Blood Clots
Hospitalization, particularly involving physical trauma, surgery,
or prolonged immobility, increases the risk for blood clots.
Physical Trauma
Injury to a vein that may be caused
by a broken bone, muscle injury, or
other serious injury to the body.
Surgery
Major surgery, particularly
of the pelvis, abdomen, hip,
or knee.
Immobility
Confined to a bed or wheelchair for
long periods of time due to a
hospital stay, injury, or illness.
Understanding Blood Clots
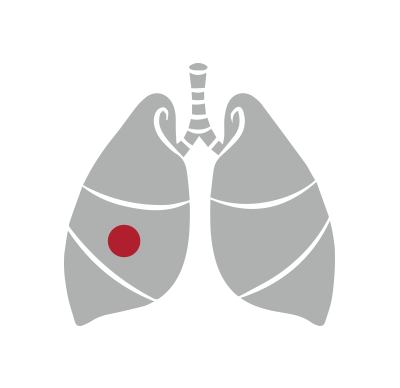
A blood clot in one of the large veins, usually in a person’s leg or arm,
is called a deep vein thrombosis or DVT. When a DVT forms, it can partially or
completely block the flow of blood through the vein.
If a DVT is not treated,
it can move or break off
and travel to the lungs.
A blood clot in the lungs is called a pulmonary embolism or PE.
This requires immediate medical attention since it can cause death.
Going to the Hospital? Get Better. Don’t Get a Blood Clot.
Have a Prevention Plan.
Have a Prevention Plan.
Before You Enter the Hospital
- Discuss your potential risk factors
and family health history with
your doctor. - Ask if you will need prevention
measures for blood clots while in
the hospital. - Make sure that all of your doctors
know your blood clot risks and
ask for a prevention plan.
Before You Leave the Hospital
- Ask your doctor how to prevent
blood clots when you are at home. - Discuss the signs and symptoms of
blood clots. - Make sure you know what to do
if you experience the signs or
symptoms of a blood clot.
When You Return Home
- Follow instructions and take
medications as prescribed. - Move around. If confined to bed or a
wheelchair, have someone help you
move your arms and legs. - Notify your doctor if you experience
signs or symptoms of blood clots.
If you experience any of the following signs or symptoms…
Blood Clots in Your Legs or Arms
Alert your doctor as soon as you can.
– Swelling of your legs or arms –
– Pain or tenderness not caused by an injury –
– Skin that is warm to the touch –
– Redness or discoloration of the skin –
Blood Clots in Your Lungs
Seek medical attention immediately.
–Difficulty breathing –
– Chest pain that worsens with a deep breath –
– Coughing, or coughing up blood –
– Faster than normal or irregular heartbeat –
To learn more about blood clots and to spread the word, visit
stoptheclot.org/spreadtheword.
stoptheclot.org/spreadtheword.
